Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMZA5PQ)
| Drug Name |
Glipizide
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aldiab; Digrin; Dipazide; Glibenese; Glibetin; Glican; Glide; Glidiab; Glidiazinamide; Glipid; Glipizida; Glipizidum; Glucolip; Glucotrol; Glucozide; Glupitel; Glupizide; Glyde; Glydiazinamide; Glypidizine; Melizide; Metaglip; Mindiab; Minidab; Minidiab; Minodiab; Napizide; Ozidia; Semiglynase; Sucrazide; Alphapharm Brand of Glipizide; Glibenese Brand of Glipizide; Glipizide Kenfarma Brand; Glucotrol XL; Kenfarma Brand of Glipizide; Lacer Brand of Glipizide; Lilly Brand of Glipizide; CP 28720; K 4024; K4024; PfizerBrand 1 of Glipizide; Pfizer Brand 2 of Glipizide; TK 1320; CP 28,720; CP-28720; G-117; Glipizida [INN-Spanish]; Glipizide Extended-Release Tablets; Glipizidum [INN-Latin]; Gluco-Rite; Glucotrol (TN); K-4024; KS-1068; Samarium(III) ionophore I; Glipizide (USP/INN); Glipizide [USAN:BAN:INN]; Glucotrol XL, Glucotrol, Glipizide; N-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]ethyl]-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide; N-(2-{4-[(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl]phenyl}ethyl)-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide; N-[2-(4-{[(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)amino]sulfonyl}phenyl)ethyl]-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide; N-(4-(beta-(5-Methylpyrazine-2-carboxamido)ethyl)benzenesulphonyl)-N'-cyclohexylurea; 1-Cyclohexyl-3-((p-(2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)urea; 1-Cyclohexyl-3-{4-[2-(5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamido)ethyl]phenylsulfonyl}urea
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Hypoglycemic Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
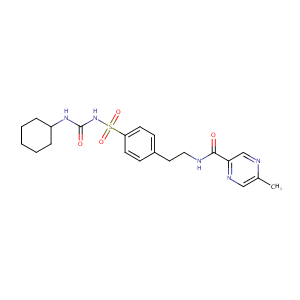 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 445.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Glipizide (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6821). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 3 | Melander A, Wahlin-Boll E: Clinical pharmacology of glipizide. Am J Med. 1983 Nov 30;75(5B):41-5. | ||||
| 4 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Glipizide 5 mg Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) - European Medicines Agency | ||||
| 7 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 8 | Triggering and amplification of insulin secretion by dimethyl alpha-ketoglutarate, a membrane permeable alpha-ketoglutarate analogue. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Apr 1;607(1-3):41-6. | ||||
| 9 | Early identification of clinically relevant drug interactions with the human bile salt export pump (BSEP/ABCB11). Toxicol Sci. 2013 Dec;136(2):328-43. | ||||
| 10 | Repaglinide : a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(6):389-411. | ||||
| 11 | Clinical consequences of cytochrome P450 2C9 polymorphisms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Jan;77(1):1-16. | ||||
| 12 | Drug-drug interactions for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase substrates: a pharmacokinetic explanation for typically observed low exposure (AUCi/AUC) ratios. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004 Nov;32(11):1201-8. | ||||
| 13 | Pharmacokinetics of chlorpheniramine, phenytoin, glipizide and nifedipine in an individual homozygous for the CYP2C9*3 allele. Pharmacogenetics. 1999 Feb;9(1):71-80. | ||||
| 14 | Initro inhibition of AKR1Cs by sulphonylureas and the structural basis. Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Oct 5;240:310-5. | ||||
| 15 | Kivisto KT, Neuvonen PJ "Effect of magnesium hydroxide on the absorption and efficacy of tolbutamide and chlorpropamide." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42 (1992): 675-80. [PMID: 1623912] | ||||
| 16 | Kivisto KT, Neuvonen PJ "Differential effects of sodium bicarbonate and aluminium hydroxide on the absorption and activity of glipizide." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40 (1991): 383-6. [PMID: 1646724] | ||||
| 17 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 18 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 19 | Bussing R, Gende A "Severe hypoglycemia from clarithromycin-sulfonylurea drug interaction." Diabetes Care 25 (2002): 1659-61. [PMID: 12196446] | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 25 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 26 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 27 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Arava (leflunomide). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
